Mechatronics Research Lab Publications
List still being populated due to webpage maintenance
2015
Aramazd Muzhikyan; Amro M Farid; Kamal Youcef-Toumi
A power grid enterprise control method for energy storage system integration Proceedings Article
In: IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Europe, pp. 1-6, 2015, ISBN: 978-1-4799-7720-8.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: intelligent systems, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids, Physical System Modeling, Simulation
@inproceedings{MRL_SG_Grid_Enterprise_Control,
title = {A power grid enterprise control method for energy storage system integration},
author = {Aramazd Muzhikyan and Amro M Farid and Kamal Youcef-Toumi},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7028898},
doi = {10.1109/ISGTEurope.2014.7028898},
isbn = {978-1-4799-7720-8},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-02-02},
booktitle = {IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Europe},
pages = {1-6},
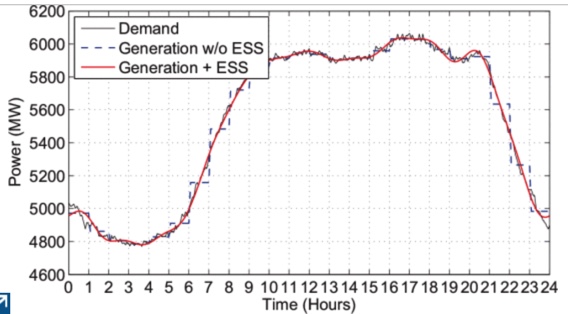
abstract = {Traditionally, power system balancing operations consist of three consecutive control techniques, namely security-constrained unit commitment (SCUC), security constrained economic dispatch (SCED), and automatic generation control (AGC). Each of these have their corresponding type of operating reserves. Similarly, energy storage systems (ESS) may be integrated as energy, load following, or regulation resources. A review of the existing literature shows that most ESS integration studies are focused on a single control function. In contrast, recent work on renewable energy integration has employed the concept of enterprise control where the multiple layers of balancing operations have been integrated into a single model to capture and potentially control the interactions between timescales. This paper now uses such an enterprise control model to demonstrate the multiple timescale effects as a consequence of ESS integration into a single control action. It also proposes a novel scheduling technique which beneficially exploits this coupling in two timescales. As a result, the ESS scheduling technique shows peak-loading shaving and operating costs reductions in the SCUC and load following reserve requirements in the SCED.},
keywords = {intelligent systems, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids, Physical System Modeling, Simulation},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2014
Aramazd Muzhikyan; A M Farid; Kamal Youcef-Toumi
An enhanced method for the determination of load following reserves Proceedings Article
In: 2014 American Control Conference, pp. 926-933, IEEE IEEE, 2014, ISBN: 978-1-4799-3274-0.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: intelligent systems, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids, Physical Systems Modeling, Simulation
@inproceedings{MRL_SG_Reserve_Quantification,
title = {An enhanced method for the determination of load following reserves},
author = {Aramazd Muzhikyan and A M Farid and Kamal Youcef-Toumi},
url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6859254&isnumber=6858556},
doi = {10.1109/ACC.2014.6859254},
isbn = {978-1-4799-3274-0},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-07-21},
booktitle = {2014 American Control Conference},
pages = {926-933},
publisher = {IEEE},
organization = {IEEE},
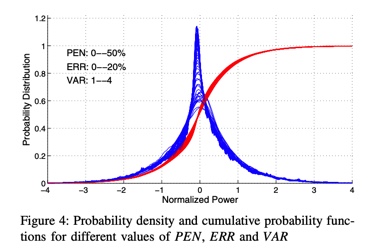
abstract = {Power generation reserves play a central role for maintaining the balance of generation and consumption. Reserves, scheduled in advance, compensate for forecast error, variability and transmission losses. However, as reserves are a costly commodity, their amount should be carefully assessed to prevent unnecessary expense. Currently, the quantity of required reserves are determined based upon a posteriori methods that use operator's experience and established assumptions. This paper instead presents a method founded upon non-dimensional numbers and digitial signal processing to determine the quantity of load following reserves a priori.},
keywords = {intelligent systems, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids, Physical Systems Modeling, Simulation},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2013
Ajay Deshpande; Sanjay E Sarma; Kamal Youcef-Toumi; Samir Mekid
Optimal coverage of an infrastructure network using sensors with distance-decaying sensing quality Journal Article
In: Automatica, vol. 49, no. 11, pp. 3351-3358, 2013, ISSN: 0005-1098.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Experimentation, Fabrication, Instrumentation, Mechatronic Design, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids, Physical System Modeling
@article{MRL_AFM_Distance_Decaying_Sensors,
title = {Optimal coverage of an infrastructure network using sensors with distance-decaying sensing quality},
author = {Ajay Deshpande and Sanjay E Sarma and Kamal Youcef-Toumi and Samir Mekid},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005109813003774},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2013.07.029},
issn = {0005-1098},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-08-27},
journal = {Automatica},
volume = {49},
number = {11},
pages = {3351-3358},
publisher = {elsevier},
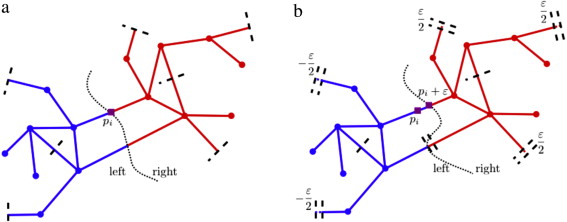
abstract = {Motivated by recent applications of wireless sensor networks in monitoring infrastructure networks, we address the problem of optimal coverage of infrastructure networks using sensors whose sensing performance decays with distance. We show that this problem can be formulated as a continuous p-median problem on networks. The literature has addressed the discrete p-median problem on networks and in continuum domains, and the continuous p-median problem in continuum domains extensively. However, in-depth analysis of the continuous p-median problem on networks has been lacking. With the sensing performance model that decays with distance, each sensor covers a region equivalent to its Voronoi partition on the network in terms of the shortest path distance metric. Using Voronoi partitions, we define a directional partial derivative of the coverage metric with respect to a sensor’s location. We then propose a gradient descent algorithm to obtain a locally optimal solution with guaranteed convergence. The quality of an optimal solution depends on the choice of the initial configuration of sensors. We obtain an initial configuration using two approaches: by solving the discrete p-median problem on a lumped network and by random sampling. We consider two methods of random sampling: uniform sampling and D2-sampling. The first approach with the initial solution of the discrete p-median problem leads to the best coverage performance for large networks, but at the cost of high running time. We also observe that the gradient descent on the initial solution with the D2-sampling method yields a solution that is within at most 7% of the previous solution and with much shorter running time.},
keywords = {Experimentation, Fabrication, Instrumentation, Mechatronic Design, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids, Physical System Modeling},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
William N Lubega; Apoorva Santhosh; Amro M Farid; Kamal Youcef-Toumi
Opportunities for Integrated Energy and Water Management in the GCC Proceedings Article
In: EU-GCC Renewable Energy Policy Experts' Workshop, Gulf Research Center, 2013, ISBN: 978-1-4799-3685-4.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: intelligent systems, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids
@inproceedings{MRL_SG_Integrated_Energy_Management,
title = {Opportunities for Integrated Energy and Water Management in the GCC},
author = {William N Lubega and Apoorva Santhosh and Amro M Farid and Kamal Youcef-Toumi},
url = {http://amfarid.scripts.mit.edu/resources/Conferences/EWN-C36.pdf},
isbn = {978-1-4799-3685-4},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-01-01},
booktitle = {EU-GCC Renewable Energy Policy Experts' Workshop},
publisher = {Gulf Research Center},
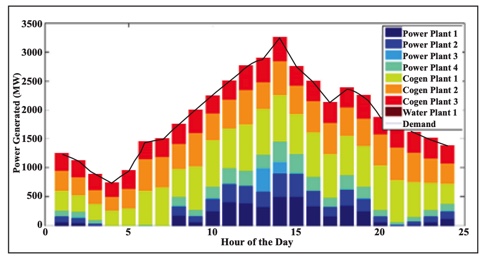
abstract = {Electric power is required to produce, treat, distribute, and recycle water while water is required to generate and consume electricity. The goal of this position paper is to identify and motivate opportunities for the operations management and planning of the energy-water nexus. It proceeds in three parts. First, an exposition of the energy-water nexus especially as it applies to the GCC is given. This discussion focuses on the electric power system, the potable water distribution system, and the wastewater distribution system. Then, the paper shifts to opportunities in operations management where recent work in the Laboratory for Intelligent Integrated Networks of Engineering Systems has produced a number of optimization programs to support the deregulated operation of integrated energy-water markets. To highlight the viability of this idea, an energy-water nexus supply side economic dispatch is presented. Finally, the position paper shifts to discuss planning opportunities for the energy-water nexus for the sustainable development of water and energy resources. These include new methods that encourage renewable energy penetration and balance the portfolio of desalination technologies. It also includes integrated strategies for the design of water infrastructure to minimize embedded energy while reusing water of various qualities. The paper concludes with a description of opportunities for EUGCC collaboration to support the purpose of the workshop.},
keywords = {intelligent systems, Modeling; sizing and control of smart grids},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
